What causes a lithium ion battery fire?
- Defective Battery
- The Environment - Too Hot or Cold
- It’s all your fault
Defective Battery
Batteries can start fires if there are defects in the components of the cell created during the manufacturing process or if the battery was damaged at some point during its lifetime that made it susceptible to shorting or thermal runaway.
What is thermal runaway?
Thermal runaway is a process when the internal battery temperature becomes too hot. If the battery gets too hot, chemical reactions inside the battery make the battery even hotter, which leads to more chemical reactions. This feedback loop eventually leads to a fire or an explosion if the temperature cannot be reduced to the normal operating temperatures.

What causes thermal runaway?
- Short circuits - internal and external
- Overcharging
- Rapid Charging
- Environmental temperatures

Battery Protection and Safeguards
The reason why some Li-ion batteries can be so inexpensive is that they lack some of the components that prevent shorts, thermal runaway, fires and explosions.
If you are unfamiliar with the inner workings of a Li-ion battery, it would be smart to follow the recommendation of the device’s manufacturer to avoid warranty issues and most importantly, starting a FIRE!
- Overcharge Protection
- Over-Discharge Protection
- Overvoltage Protection
- Overcurrent protection
- Short-circuit protection

Many of these protection mechanisms are located directly on the circuit board inside the battery. If the battery does not include all the necessary and expensive components, the battery will be more dangerous to operate and charge. Be careful purchasing off brand batteries because their lower prices indicate they lack some of these protection mechanisms.
Rapid charging
There are different amounts of current that a battery can draw. The faster you charge the battery, the hotter the battery will get. Keep this factor in mind when charging older batteries. If the battery’s casing is damaged, or the battery has been dropped from a height, the chances of shorting or thermal runaway is greater. Unchecked thermal runaway leads to the battery catching fire, remember?
Environmental temperatures
The standard operating temperature range for Li-ion batteries is around -20°C to 60°C, some have special features that can extend this range in both directions. That means the battery can discharge and operate a device at “normal” temperature ranges, however charging the battery below freezing could damage the battery.

Charging a lithium-ion battery below the freezing point
You should never charge a lithium-ion battery below the freezing point. Charging a lithium-ion battery below freezing will cause lithium plating and dendrites. Dendrites will cause a short-circuit internally that can cause a fire or an explosion.
When to replace a lithium ion battery?

- Lithium-ion batteries should be replaced if you see rips, tears, or holes in the casing of the battery. There is a chance that the battery could short, causing a fire.
- Lithium batteries have a lifespan of about 3-5 years in storage. You should consider replacing the battery after 300-500 charge cycles or after 3-5 years if unused.
How to lengthen the lifespan of your rechargeable battery?
- Never leave your battery with zero charge.
- Never leave your battery fully charged
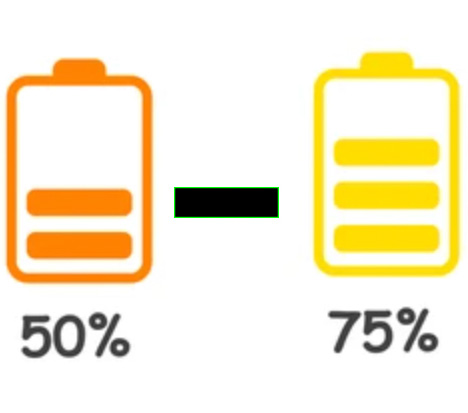
- Leaving your battery at 50%-75% charge will keep your battery working longer
Why storing your li-ion battery without a charge is potentially dangerous
A 21700 battery when fully charged operates at 3.6 volts and if it includes an over-discharge protection it will drop to 2.5V when “fully” discharged. The battery technically still holds a charge at 2.5V however some high drain devices will not function properly if the integrity of the current is reduced.
The reason why the battery doesn’t completely use all its available power to 0 volts is that the battery will degrade to the point where it cannot hold any charge if it gets too low, so the
manufacturers have built-in an over-discharge circuit that prevents the battery from dropping below 2.5 volts in the 21700 battery.
If left in this state with no or low power, the materials inside the battery will start to wear each other out. If the battery has been damaged enough in this dormant state, then the possibility of overcharging the battery or shorting the battery increases. This internal damage caused by what happens to the battery when left with no charge for long periods of time could lead to swelling of the battery when charging, which could start a fire or cause an explosion.
If the battery capacity reduction rate changes based on available energy, and the capacity reduces faster when it is considered “fully” discharged, then the battery capacity reduction rate continues to accelerate the lower the battery gets. The more time you leave your dead battery laying around, the faster it will lose capacity.
If a battery is stored for 2 years, the second year has a greater impact on reducing the capacity of the battery than the first year.
When to recycle a Lithium-ion battery
- Recycle your battery if the charge time takes longer than it should
- If your battery is swelling after recharging
- If your battery is 5 years old
- If your battery cannot hold a charge
- If your battery has holes, tears, or is lose at the ends
- You have recharged the battery 300-500 times

